How to Write a Research Paper
Writing Guide
When it comes to writing such a work, many students find it hard to even start working on it. But why? Why are research papers so scary to students?
Well, the answer is that this type of assignment is much more complicated than a regular high school or college essay, as it implies taking many steps.
Definition
A research paper is a widespread type of academic work that many students of various specializations have to do throughout their academic years. The name of the assignment speaks for itself, as the research performed based upon the work of other authors, scientific experiments, or academic examples is the main component of such a work.
In many colleges, such papers are an essential part of the study process. As almost every college student will have to perform such work at least once, it’s crucial to know what steps one should take and what elements to work on.
The main challenges that a student might face when starting a research paper might be:
- To find an excellent idea
- To adjust the topic if needed (if the topic is too narrow or too broad to find the proper number of sources and the right information)
- To find and analyze primary and secondary sources
- To organize collected data
- To write and edit the work
These are not the easiest tasks. However, the following guide will help you get through each of them without struggling.
Types
As you probably know, there are a lot of various types of essays that students perform in high school and college. Research papers also vary in forms and purposes. Let’s take a look at the most common research papers and their specifics.
There are two major types of such works:
Argumentative/Persuasive research paper – a project which must exhibit the author’s position on some debatable topic and provide evidence to support the suggestions and claims. The majority of topics for such a type of paper are phrased in the form of a question with two or more possible (and usually polar) positions the author should pick to base their research on.
Analytical research paper – the main aim is to analyze various facts, points of view, and evidence from different sources to make a personal conclusion. Analytical papers can be written on almost any topic if there is enough information to collect.
Other types:
Definition – describes facts and evidence solely for informative purposes. It doesn’t imply analyzing information or expressing opinions.
Cause and effect – its purpose is to analyze a topic and provide answers to the questions “What?” and “Why?” While working on such a paper, it’s important to find the relationship between actions and results.
Experimental – aims to perform an experiment (or take an experiment performed by someone else) and analyze the experience, findings, and observations to come up with a conclusion about the nature of the phenomena or its possible impact.
Interpretive – an assignment that implies putting theoretical knowledge into a particular case study providing author’s interpretation and critical analysis.
Compare and contrast – a paper based on the analysis of (usually) two objects of the study side by side to find their similarities and differences. For example, you might need to compare two authors or two ideologies to find what their touching points are.
Reports – are based on a specific case study. Their purpose is to provide a summary of the situation, its main issues, and recommendations. Such papers are usually assigned in sociology classes.
Steps of Writing
Every research paper is unique, and the process of its creation varies depending on the topic of the study. However, there is also a general plan which consists of five steps.
Step 1 – Preparation
Every paper begins with defining the topic and the main points that the author is going to cover in the work. This is the step when you have to decide what problem or question you will address in your work and conduct research on it.
Pick the Topic
Make sure to pick a topic that is not too narrow or too broad as it will be difficult for you to find the needed information for your study.
A few research paper topic examples:
- Ethical dilemmas of cosmetic surgeries
- The influence of the body positivity movement on the obesity problem
- Should schools prevent and punish cyber-bullying?
- Should the government legalize marijuana?
- Pros and cons of using pesticides
- The wage gap in the 21st century
- How did technological races change the world?
- The influence of the Black Plague on the economics of Europian countries.
- Microchips: should they be used on people?
- How does social media influence social anxiety?
- Should it be harder to get a divorce?
- The influence of video games on the crime level
Draft Your Thesis Statement
You might draft it now or put it aside until you find more information on your topic – it doesn’t really matter. Remember that a good thesis statement sums up your idea into one or two sentences. This is the core – the statement that is supported by the whole study. Everything in your work should agree with your point and provide evidence for it.
Example:
“Though the Cold War was a period of conflict and tension, it made dramatic changes in the fields of technology and science such as space mission launches, the invention of the Internet, and the development of nuclear technology.”
Step 2 – Conduct Your Research
Once you decide what topic you want to cover in your study, you can start collecting and analyzing data from various sources. This process takes a lot of time due to tons of information that you should look through and decide if it makes a good fit for your research paper. There are also some general tips that might come in handy:
- Make sure you take information from reliable sources only. There is nothing worse than putting doubtful data into your research, as it will affect your result and will cause questions from your professor. So, make sure to look up the sources of data you are using – academic journals from scholarly databases (JSTOR and EBSCO), books from your library or Google Books, government publications, websites recommended by your learning institution, etc.
- Always write down the source, page number, and the author of the quotes while you are taking notes – this way, you won’t have to go back and look for where you took that fact from.
- Eliminate the sources that repeat information – don’t waste your time.
When you search for information on your topic, it’s crucial to write down everything you find relevant and useful. It might look like a mess at first, but you can organize it later and bring all the pieces together.
Step 3 – Create an Outline
The outline is an important part of any paper. It helps you structure it and makes sure you don’t forget anything important to mention. Moreover, by creating an outline (even a rough one) and writing down the main points that you will cover in each part of your paper, you will see if you have enough evidence to prove your point.
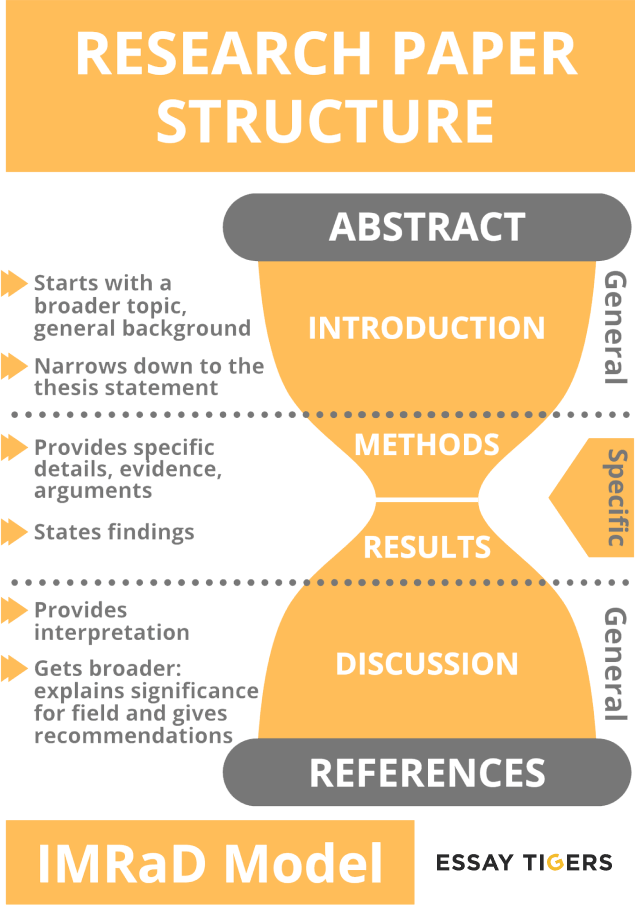
A typical research paper consists of the following parts:
Title/Cover Page
The title is the first thing that a reader of your piece sees, and its main purpose is to specify the object of the study and provide other useful information about the author and the research such as, for example, year of submission, co-authors, and the learning institution.
Abstract
The abstract is a quick explanation of your work that includes information about:
- The specific problem your piece is addressing
- The methods and materials you are using
- The main findings or results of your study
- The conclusion (suggesting ways to solve the problem, stating possible importance of your study, etc.)
Remember, the abstract should be brief and informative. This is not the place for various visuals and detailed explanations or discussions.
Introduction
This is the part that introduces the broader topic, the background of the study, and then narrows it down to the specific object, question, or problem that is addressed in the work. It also describes the purpose of the research and its aims.

The Main Body
The largest part of your work is the main body. It is the chapter where you provide the arguments and evidence that support your thesis statement. Depending on the requirements of your learning institution, the structure of the main body might vary. Generally, the main body consists of the following parts:
- Materials/Literature review – the analysis of previous works, theories, and relevant experiments.
- Methodology – a detailed explanation of what exact steps you took. This is for a reader to be able to replicate your study if needed.
- Results – key findings of the research.
- Discussion – addresses your interpretation of the findings and their importance, and possibly a recommendation for further research.
Conclusion
The conclusion is an essential part of any paper as it summarizes all the work and restates the thesis statement. It also provides a synthesis of the key points and arguments presented through your work.
References/Bibliography
This part lists all the works that you are using in the process of creating your research paper. Depending on the formatting style of your paper, it might be formed differently.
Step 4 – Draft Your Paper
Start with organizing all your resources and notes. This will give you direction and a starting point for your draft. If you find starting with an introduction a bit hard (which is not rare), you can start with the body paragraphs.
When getting to the part where you present your arguments and evidence, start with the strongest one, and then go through the less important or weaker arguments. Remember that each paragraph should follow the common pattern:
- Topic sentence that gives an understanding of the content of the paragraph.
- A supportive sentence. This is the part where you should provide evidence and the explanation of why it is relevant and how it fits your thesis.
- A conclusive and a transition sentence.
Sticking to this structure of your paragraphs helps you make your paper easy to read and keep the logical flow without repeating yourself or jumping from one fact to another without proper analysis.
Step 5 — Revise and Edit Your Draft
Reread your draft carefully. You might have to do this a few times because while revising you need to:
- Check if there are any content or grammar errors.
- Check if the facts and quotes are correct.
- Check the cited sources.
Sometimes the revision might show that you weren’t clear enough in your arguments or didn’t word them properly. In this case, you will need to fix these mistakes and reword the sentences that aren’t strong enough.
If you are not sure about your spelling or punctuation, use grammar checks such as Grammarly that will bring attention to misspelled words or missing commas. However, a professional team of experts can do much more for your piece by editing and polishing it or even writing a research paper from scratch.
Step 6 – Finish and Submit Your Work
After editing, it’s good to reread your paper one more time and make sure everything is flawless. If you have some time before the deadline, you can put your work aside and come back to it a few hours later – fresh eyes are very useful when critically looking through your work.
Make sure you fulfill the requirements regarding word count and formatting, print your paper, or submit it via email. These were the best tips on research paper writing for you. Good luck with your assignment.

